Installing EV Charging Stations at Shared Homes
This guide delves into the process and considerations for installing electric vehicle (EV) charging stations in shared residential spaces. Installing charging stations in shared residences, such as condominiums or apartment buildings, involves addressing logistical, legal, and technical challenges, including parking rights and wiring infrastructure.
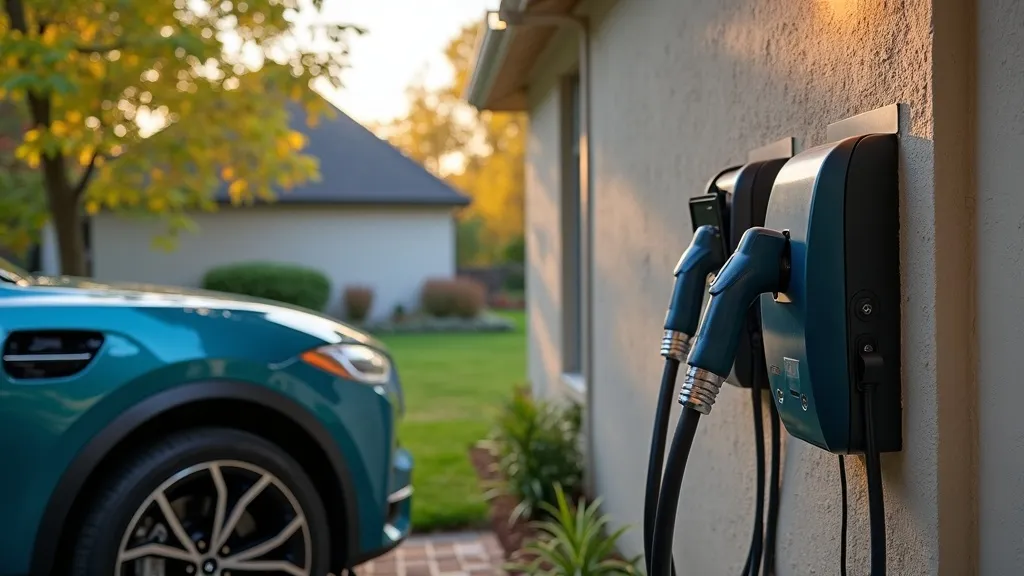
Installing EV Charging Stations in Shared Residences
The shift towards clean and sustainable transportation is driving an increased demand for electric vehicles (EVs) globally. Consequently, the need for adequate and accessible charging infrastructure is becoming more critical, especially in shared residential environments. This article explores the essential considerations and steps for התקנת עמדת טעינה לרכב חשמלי בבית משותף (installing an EV charging station in a shared residence) and provides comprehensive guidance to residents and property managers.
Understanding the Basics of EV Charger Types
Before embarking on the installation process, residents need to comprehend various aspects, including the type of charging stations, the local regulations governing shared properties, and the infrastructural requirements. There are primarily three main types of electric vehicle chargers: Level 1, Level 2, and DC Fast Chargers.
Level 1 Chargers: Typically utilize a standard 120-volt outlet, providing a slow charge and typically suited for home use where the vehicle can charge overnight. They are not ideal for shared residences due to their inefficiency.
Level 2 Chargers: Known for their efficiency, these chargers operate on a 240-volt outlet and can significantly reduce charging time. This makes them the most suitable choice for shared residences, offering faster charging capabilities compared to Level 1 chargers, making them ideal for those who may have limited time to charge.
DC Fast Chargers: These are mostly found in public charging stations and are capable of charging vehicles significantly faster than the Level 1 and Level 2 options. However, they are usually expensive to install and maintain and not commonly suited for residential settings.
Understanding these options is vital for residents because the choice of charger will influence installation costs, necessary electrical upgrades, and potential collaboration with the homeowners’ association.
Addressing Legal and Ownership Concerns
Shared residences, by nature, involve multiple stakeholders, making it crucial to navigate the legal implications and secure consensus among all parties. This includes acquiring the necessary permissions from the homeowners' association or property management, which typically governs most shared residential spaces. Establishing ownership and maintenance responsibilities early on can prevent potential disputes.
Before starting the installation process, it is vital for residents to consult the governing documents of their homeowners’ association. These documents often outline the rules concerning modifications to shared areas, including the installation of charging stations. Clear communication with fellow residents is also essential to gauge interest in installing charging stations and fostering a collaborative environment to support the initiative.
Moreover, it is advisable to draft a usage agreement that outlines how the charging station will be used, the costs associated with installation and maintenance, and the method for dividing costs among resident users. This will provide a clear framework for regular operations, responsibilities, and expectations, helping avoid misunderstandings down the line.
Technical and Logistical Considerations
From a technical perspective, an essential step in installing an EV charging station involves assessing the building’s electrical capacity to support the additional load. An electrical contractor should conduct a comprehensive evaluation to determine if an upgrade is necessary. The additional power required for charging stations can significantly impact the overall load management of the building's electrical system, and thus must be analyzed thoroughly.
Some properties may require upgradation of their electrical infrastructure, which might include:
- Rewiring sections of the building
- Upgrading transformers
- Adding or upgrading circuit breakers
- Expanding the electrical service line
These upgrades are significant investments and should be factored into the overall project budgeting.
Logistical factors such as the proximity of parking spaces to electrical outlets and the need for wiring enhancements should also be considered. The installation needs to be as convenient as possible for regular use, minimizing the need for excessive cabling and ensuring safe access to the charging stations. Ensuring adequate signage and clear access routes is also essential for both pedestrians and drivers.
Leveraging Sustainable Energy Solutions
Integrating solar energy solutions can enhance the sustainability of EV charging stations. In countries with robust solar incentives, such as the U.S., homeowners can benefit from various government-funded solar programs that can also indirectly support EV infrastructure. Below is a comparative table featuring resources on affordable solar panels in English-speaking countries:
| Provider | Focus | Website |
|---|---|---|
| Renogy | Solar panels and accessories | www.renogy.com |
| Solar Panel Store | Diverse solar products | www.solarpanelstore.com |
| SolarReviews | Information on solar panels and installers | www.solarreviews.com |
Source: Renogy, Solar Panel Store, SolarReviews
Utilizing solar-powered solutions means that not only can the charging stations be powered sustainably, but users can also reduce their reliance on grid power, leading to reduced utility bills. However, it is important to account for variability in sunlight availability based on location and seasons. For this reason, a hybrid system using both grid power and solar energy may be the most effective approach for many shared residences.
Utilizing Government Incentives
Numerous government incentives can assist in the installation of solar panels, which are integral to powering EV charging stations sustainably. Tax credits, rebates, and net metering programs are available in many regions, making the transition to solar energy more financially feasible. Homeowners and associations should investigate these opportunities to offset installation costs. Common types of incentives include:
- Federal Tax Credits: Often allow homeowners to deduct a percentage of the cost of solar installation from their federal taxes.
- State and Local Incentives: Many states offer their own incentives, such as cash rebates or state tax credits, which can significantly reduce upfront costs.
- Utility Incentives: Some utility companies offer rebates for solar panel installation, as well as programs to buy back excess energy generated by solar systems.
- Grants and Subsidies: Various non-profit organizations and government bodies may provide grants aimed at promoting renewable energy installations.
Researching and applying for these incentives collectively, as a community, can enhance financial benefits for all parties involved, making it easier and more affordable to install charging stations with a sustainable energy source.
Incorporating Smart Technology in Charging Stations
As technology continues to evolve, incorporating smart charging stations into shared residences can provide multiple benefits, including enhanced user experience, efficiency improvements, and ease of management. Smart charging stations can offer features such as:
- Remote Access and Management: Users can monitor and manage their charging usage from smartphones, including scheduling charging times to optimize electricity rates. This feature is particularly beneficial for residences utilizing time-of-use electricity rates.
- Load Management Capabilities: Smart charging stations can communicate with the building's electrical system to ensure balanced power distribution, preventing overload during peak demand times.
- Data and Analytics: Users can track their charging habits and energy consumption over time, enabling better budgeting and energy usage awareness.
- Built-in Payment Systems: Residents can utilize integrated payment solutions, allowing for easy billing management and potentially even income generation through offering charging services to non-residents.
The inclusion of smart technology can enhance user satisfaction, optimize costs, and increase the overall efficiency of the EV charging network within shared residences.
FAQs
- Q: What type of charging station is recommended for shared homes?
A: Level 2 chargers are typically recommended for efficiency and faster charging times within residential communities due to their adaptability for home installations. - Q: What are some potential challenges during installation?
A: Legal permissions, electrical capacity evaluation, logistical arrangements for wiring, and parking space configurations are common challenges, but overcoming them is crucial for successful implementation. - Q: Can solar energy offset the costs?
A: Yes, integrating solar panels can reduce operational costs, while various government programs offer incentives for adopting solar solutions, making the investment more accessible. - Q: How can smart technology benefit charging stations?
A: Smart features enable remote management, load balancing, data tracking, and integrated payment systems, enhancing user experience while optimizing energy use in the shared environment.
In conclusion, installing an EV charging station in a shared residence requires careful planning and collaboration among stakeholders. Addressing technical, legal, and logistical facets is crucial for a smooth installation process. Exploring sustainable energy opportunities, like solar panels, can further enhance cost-effectiveness and sustainability. With the ongoing evolution of EV technology and infrastructure, embracing these modern developments may position shared residences at the forefront of sustainable urban living.
As the demand for electric vehicles continues to grow, the importance of accessible charging infrastructure in shared spaces is undeniable. Focused discussions and collaborations can lead to successful implementation, ultimately transforming residential communities into more eco-friendly environments.
Disclaimer: The information provided herein is based on resources available online as of October 2023. For the most accurate and up-to-date information, please refer to official websites, local regulations, and professional guidance specific to your area.
-
1

Ultimate Feast for the Eyes: Top Cooking Shows Every Foodie Must Watch!
-
2

Maximize the Lifespan of Your New Dental Implants with Expert Care Tips
-
3

Ascending with Ease: The Revolutionary Journey of Stair Lift Technology
-
4

Maximizing Your Walk-In Tub's Lifespan: The Ultimate Guide to Enhanced Performance and Durability
-
5

Unlock Bigger Savings: Master the Art of Using Your Gas Rebate Card!






